Introduction
The writing spider is one of the many fascinating creatures that abound in the natural world. This intriguing arachnid, also called Argiope aurantia or the black and yellow garden spider, has piqued people’s interest for many years. The writing spider is not simply a garden pest—it is a subject of folklore, scientific curiosity, and creative inspiration due to its unique web patterns and attractive look. We will delve deeply into the world of the writing spider in this blog post, covering everything from its biology and behavior to the cultural significance it has around the globe.
What Is a Writing Spider
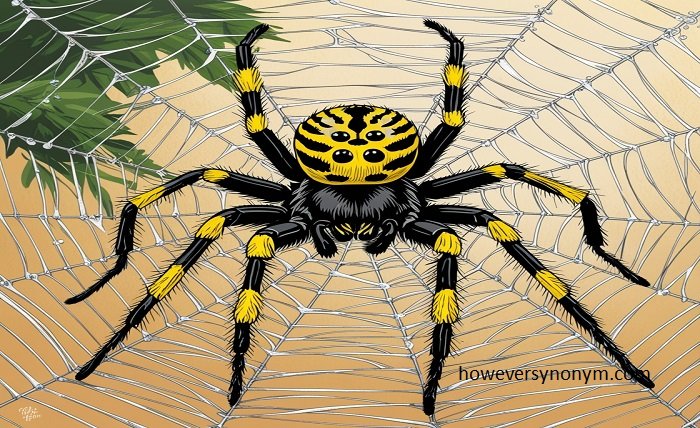
writing spiders, orb-weaver spiders, are members of the Araneidae family, which includes the scientifically named Argiope aurantia. These spiders are renowned for weaving elaborate, massive webs that are visually arresting in addition to being useful. The word “writing spider” refers to the distinctive zigzag pattern, known as a stabilimentum, that is present in the middle of their webs. This pattern is similar to writing or script, which has long captivated and perplexed onlookers.
Physical Characteristics of the Writing Spider
The distinctive black and yellow coloring of the writing spider makes it easy to identify. With body lengths ranging from 0.75 to 1.1 inches, female writing spiders are significantly larger than men, with males typically measuring between 0.2 and 0.35 inches. The females have longer, more robust legs with black and yellow bands, giving them a distinctive and slightly menacing aspect. Due of their smaller size and lack of color, males are frequently overlooked in the wild.
Habitat and Distribution
North America is home to the majority of writing spider, particularly in the southern regions of the United States and Canada. They do well in fields, gardens, and other places where they may weave their webs between trees or other structures with ease. These spiders like open, sunny spaces that are full of insects for prey. They are frequent in human-occupied areas like yards and gardens, but they are also common in meadows and woodlands where there is plenty of flora to make webs.
The Web: A Masterpiece of Nature
The writing spider’s web is a remarkable invention. It is huge, frequently measuring more than two feet in diameter, and is made up of radial lines connecting concentric circles. The stabilimentum, or the zigzag pattern that runs through the middle of the web, is what makes it so unique. Scientists are still at odds over the precise function of this pattern, but it’s thought to have several uses, including supporting the web, luring prey, and even discouraging predators. Additionally, according to some hypotheses, the stabilimentum increases the web’s visibility to birds, which lessens the chance that it will be destroyed.
Behavior and Hunting Techniques
Due of their diurnal nature, writing spider are active during the day. They use spider webs to capture prey, making them sit-and-wait predators. When an insect becomes entangled in the sticky silk, the spider moves swiftly to ensnare its victim, renders it immobile with venom, and wraps it in silk to be eaten later. The venom of the writing spider is strong against small insects but innocuous against people, causing only minor discomfort in the rare event of a bite.
The Life Cycle of the Writing Spider
The writing spider’s life cycle starts with mating, which usually takes place in the latter part of summer. The male spider approaches the female warily, frequently making a little web next to hers and vibrating repeatedly to let her know he is there. The female attaches her silken sac containing the eggs to the web or another adjacent surface after mating. Hundreds of eggs may be contained in this egg sac, and they will hatch the following spring.
The Role of Writing Spiders in Ecosystems
One of the most important factors in managing insect populations is writing spiders. Through their ability to feed on a wide range of insects, such as grasshoppers, flies, and even tiny wasps, they contribute to the preservation of environmental equilibrium. Gardeners frequently enjoy their presence in gardens because they help control nuisance insects that might harm crops and decorative plants. Moreover, other tiny species find refuge in the webs of writing spiders, which enhances the region’s biodiversity.
Writing Spider in Popular Culture
The writing spider has appeared in a number of popular media, such as video games, books, and movies. The character Charlotte in E.B. White’s beloved children’s novel Charlotte’s Web is based on a writing spider, making it one of the most well-known allusions to the writing spider. Similar to how a real-life writing spider’s stabilimentum makes patterns that have captured people’s attention, Charlotte utilizes her web to communicate in the book.
Conclusion
People from many walks of life have been captivated by the amazing writing spider for a long time. The writing spider has a crucial function in managing insect populations and creating beautiful web patterns, making it an essential component of the natural world. We can cultivate a greater regard for the diversity of life around us by learning about and developing an appreciation for these spiders.
FAQ
Are writing spiders dangerous to humans?
No, writing spiders do not pose a threat to people. Although their venom is efficient against their insect food, humans are not seriously threatened by it. Rarely, bite victims will experience modest symptoms like localized discomfort and redness.
Why is it called a writing spider?
The stabilmentum, or zigzag pattern, in the middle of the writing spider’s web is what gives it its name. The term comes from the pattern’s resemblance to writing or script. read about more disney 100 lorcana.
What do writing spiders eat?
The main food source for writing spiders is insects, such as wasps, grasshoppers, and flies. They use spider webs to capture prey, render it immobile with venom, and then eat it.